CityPay Elements
CityPay Elements is a secure, embeddable set of web components for accepting card payments (and selected alternative payment methods) in your web application. It encapsulates card data entry into isolated, CityPay‑hosted iframes, tokenises card details client‑side, orchestrates 3‑D Secure (3DS) when required, and integrates cleanly with your backend via Payment Intents.
Elements is designed for developers building modern payment flows who want strong security guarantees without sacrificing control over the customer experience. It provides pre-built payment components and a well-defined API, while leaving layout, validation, business logic, and user experience decisions firmly in your control.
Security model: When using Elements as intended, sensitive cardholder data is collected and processed only within CityPay-controlled environments. Card details never pass through merchant servers, significantly reducing PCI DSS scope while preserving flexibility in how checkout flows are implemented.
- PCI DSS scope reduction through CityPay-hosted iframes and client-side tokenisation.
- Built-in 3D Secure (3DS) with automatic frictionless and challenge flows.
- Payment Intent lifecycle with explicit states and retry support.
- Event-driven integration via structured client events (
cpe:*). - Configurable automation for common flows (for example
autoHandle3DS,autoAuthorise).
This guide shows the fastest way to accept a card payment using CityPay Elements in Direct Mode.
By the end, you will have:
- created a Payment Intent
- mounted a hosted card form
- tokenised card details in the browser
- attached the token to the intent
- confirmed the intent (handling 3DS when required)
- authorised (and optionally captured) the payment from your backend
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- a CityPay account
- a Client Licence Key for server-to-server requests (backend only)
- a Public Key for browser initialisation (safe to embed)
- a backend capable of:
- creating Payment Intents
- performing authorise (and capture if applicable)
- a working HTTPS environment (local dev is fine)
Security: Never expose your Client Licence Key in browser code. The Public Key is safe to embed and must be paired with a Session Token generated for the Payment Intent.
1) Create a Payment Intent (backend)
Create the Payment Intent on your backend. This declaratively represents your intent to take payment and can support multiple attempts over time.
// Pseudocode – replace with your CityPay API client call
const intent = await citypay.paymentIntents.create({
merchantid: 1000023000,
amount: 1999,
currency: "GBP",
billTo: {
title: "Mr",
firstname: "N",
lastname: "Person",
email: "n.person@example.com",
// ...
},
idempotencyKey: '...',
identifier: "order_123"
});
return { intentId: intent.id };
2) Initialise Elements and mount the card form (frontend)
Install via npm or load via a script tag. This example assumes a module install.
import { CityPayPromise } from "@citypay/sdk";
const intent = {} // created in backend
const api = await CityPayPromise({});
const elements = api.elements({
pubKey: 'XXZZYY...',
})
const card = elements.cardElement("default", {
element: "#card-form",
layout: "stack",
});
await card.init();
await card.awaitReady();
3) Tokenise the card details (frontend)
const token = await card.tokenise();
4) Attach the token to the Payment Intent (frontend)
await card.attach({
intentId,
token
});
If the attach fails, prompt for a new payment method or allow retry (depending on the error).
5) Confirm the intent and handle 3DS if required (frontend)
const confirmResponse = await card.confirm({
intentId,
autoHandle3DS: true
});
If authentication is required, Elements will automatically present the 3DS challenge (when autoHandle3DS: true) and continue once complete.
6) Authorise (and capture if applicable) (backend)
Authorisation and capture are always performed server-side using your Client Licence Key.
// Pseudocode – replace with your CityPay API client call
const auth = await citypay.payments.authorise({
intentId,
// any additional order metadata you require
});
// Optionally capture if using manual capture
// await citypay.payments.capture({ intentId });
return auth;
7) Listen for events and update your UI (frontend)
Wire up events to drive spinners, error messages, and success states.
card.on("cpe:ready", () => {
// enable pay button if form is complete
});
card.on("cpe:processing:start", () => {
// show spinner, disable submit
});
card.on("cpe:processing:end", () => {
// hide spinner, re-enable submit if needed
});
card.on("cpe:error", (e) => {
// show a user-friendly error message
// never log tokens or 3DS artefacts
});
Expected lifecycle (typical)
A typical successful flow will transition through states such as:
openrequires_payment_methodrequires_customer_confirmationrequires_customer_authentication(only if 3DS is required)requires_authorisationsucceeded(orrequires_captureif capture is deferred)
Next steps
- Review Payment Intent lifecycle & states in the Definitions section.
- Implement the minimum recommended security controls (CSP, frame-ancestors, logging hygiene) before production go-live.
With a few lines of code you’ll:
- Mount a ready‑to‑use card form (or individual hosted fields).
- Tokenise the card details in the browser.
- Attach the token to a Payment Intent.
- Confirm the intent and let Elements handle 3DS if needed.
- Authorise via your backend, then capture or auto-capture funds per your settlement policy.
- Developers & integrators building bespoke checkout flows in modern frameworks (React, Next.js, Vue, plain JS).
- Solution architects who want predictable payment state machines and clean separation of duties between browser and server.
- Security & compliance teams seeking a clearly scoped integration that aligns with PCI DSS v4 expectations.
- On page: You embed a CityPay card form or hosted fields. The sensitive inputs live inside CityPay-hosted iframes. The browser never sees raw PAN data outside those frames.
- In browser (with optional middleware):
- By default, the SDK can call CityPay directly using the Domain Key. Methods such as
attach()andconfirm()are posted to CityPay over HTTPS. - You may instead configure middleware endpoints (relative URLs). In this mode, the SDK calls your backend first, and your backend forwards those requests to CityPay using your API Key.
- Middleware can be applied selectively: you might handle only
attach()through your backend, while lettingconfirm()go direct, or vice-versa. - Your backend:
- Always creates and tracks Payment Intents.
- Always performs the authorise step and decides when to capture or auto-capture funds.
- May also handle attach and confirm if you’ve configured middleware, giving you observability, logging, and compliance control.
- CityPay services: Handle 3-D Secure orchestration (frictionless or challenge), intent state transitions, and authorisation routing. Whether called directly or via middleware, the same secure APIs are invoked under the hood.
- Hosted card fields (ready‑made card form or composable inputs)
- Tokenisation & device fingerprinting
- 3DS flows (frictionless + challenge)
- Explicit intent states & idempotent flows
- Event model for telemetry, UX, and retries
- Optional auto‑flows (
autoHandle3DS,autoAuthorise) - Support for MOTO (Mail Order / Telephone Order) where 3DS is not applicable
- Foundation for vaulting (token reuse, subject to merchant configuration)
- Payment Intent – a stateful payment object that moves through creation, confirmation, (optional) customer authentication, authorisation and capture.
- Token – a single‑use surrogate for card details, created by Elements in the browser.
- Confirm – the action that requests any required customer authentication (3DS).
- Authorise – the server‑side step that reserves funds.
- Capture – the server‑side step that transfers funds (immediate or deferred).
| Mode | Pros | Cons | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Middleware (SDK posts to your backend, API Key forwards to CityPay) | • Maximum security – no Domain Key in browser • Centralised logging, retries, observability • Full control over attach/confirm routing • Easier to extend with custom orchestration | • Requires backend endpoints (e.g. /attach, /confirm)• Slightly more development effort initially | Production-grade builds, larger teams, strict compliance environments |
| Fallback (SDK calls CityPay directly with Domain Key) | • Fastest integration path • Fewer backend endpoints to implement • Ideal for demos, pilots, or rapid prototyping | • Domain Key lives in browser (short TTL, origin-bound) • Limited backend visibility and control • Harder to enforce custom policies or logging | Small teams, proof-of-concept builds, rapid go-live scenarios |
| Step | Middleware (API Key on backend) | Fallback (Domain Key in browser) |
|---|---|---|
| Initialise | elements.init({ middleware: { basePath: '/api/payments' } }) | elements.init({ domainKey }) |
| Create Intent | Backend creates intent with API Key → returns intentId to browser. (Optionally: accept token + create intent in one middleware call.) | Backend creates intent (same as Middleware). |
| Tokenise | Browser (Elements iframe) → returns token (PAN never hits merchant). | Browser (Elements iframe) → returns token (same). |
| Attach | Browser → Merchant: POST /api/payments/attach → Backend → CityPay with API Key. | Browser → CityPay: attach({ intentId, token }) using Domain Key. |
| Confirm | Browser → Merchant: POST /api/payments/confirm → Backend → CityPay with API Key. Backend returns 3DS payload/session to browser. | Browser → CityPay: confirm({ intentId, autoHandle3DS? }) using Domain Key. |
| 3DS UI | SDK renders challenge in the browser using payload returned by backend (if needed). | SDK renders challenge in the browser automatically (if needed). |
| Authorise | Backend → CityPay with API Key (always backend). | Backend → CityPay with API Key (always backend). |
| Capture | Backend immediate or delayed per policy. | Backend immediate or delayed per policy. |
| Idempotency | SDK generates a per-flow key; backend should forward it as X-Idempotency-Key on every backend→CityPay call. | SDK generates a per-flow key; CityPay honours it on confirm. Backend must reuse it for authorise. |
| Credentials used | Browser: none (only hits your /api paths)Backend: API Key (create, attach, confirm, authorise, capture) | Browser: Domain Key (attach, confirm) Backend: API Key (create, authorise, capture) |
| Network paths | Browser ↔ Merchant (all) • Merchant ↔ CityPay (all) | Browser ↔ CityPay (attach/confirm) • Browser ↔ Merchant (checkout data) • Merchant ↔ CityPay (create/authorise/capture) |
| When to choose | Maximum control, observability, retries, and compliance. Best for production-grade builds. | Fastest go-live; minimal backend work. Good for pilots, POCs, or rapid timelines. |
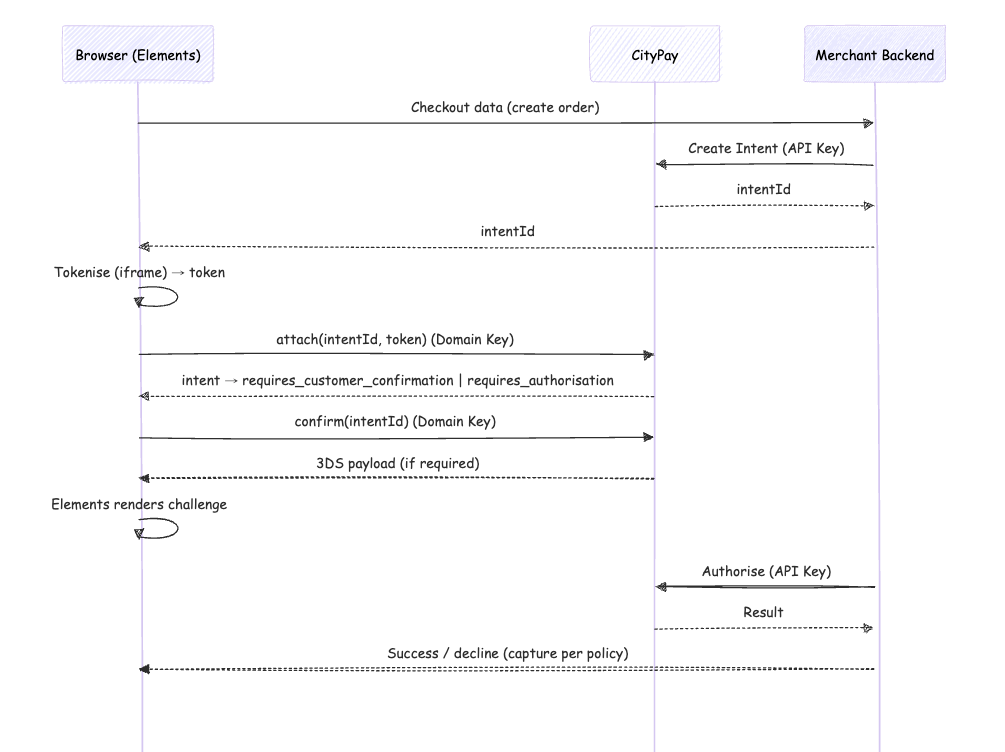
Fallback Mode
- Browser calls CityPay directly using a Domain Key.
- Fastest to implement, but requires careful Domain Key scoping (origin-bound, short TTL).
- Authorise is always backend-only using the API Key.
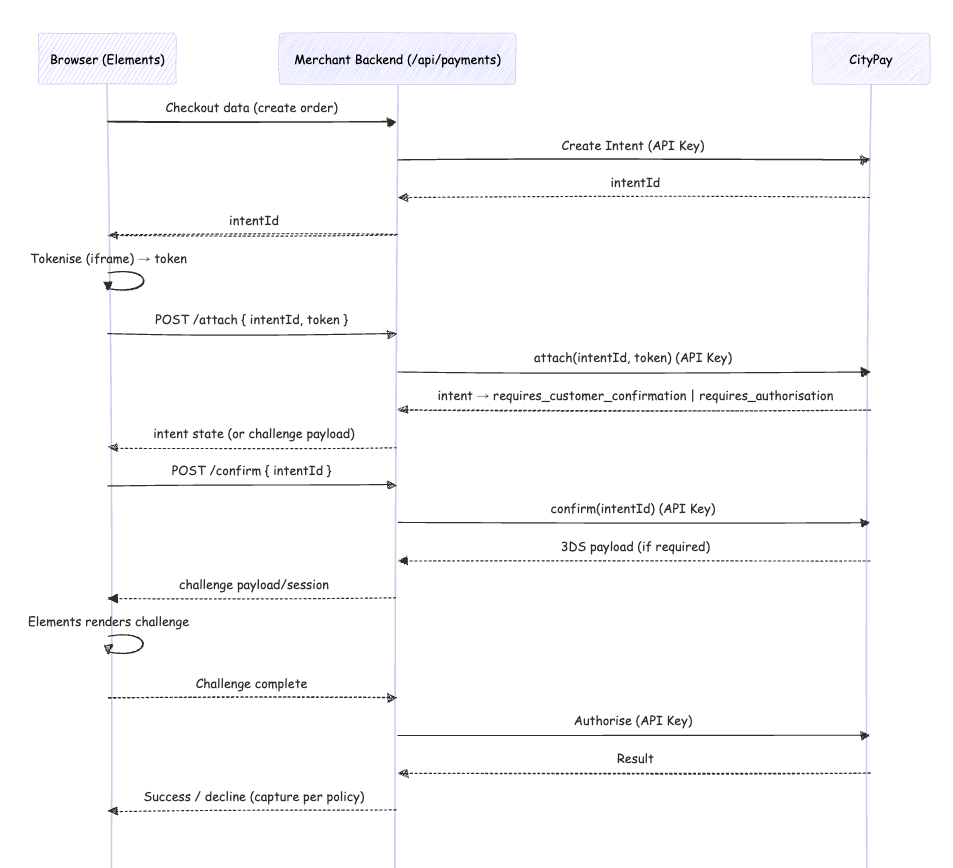
Middleware Mode
- Browser calls your backend endpoints (e.g.
/api/payments/attach). - Backend forwards the request to CityPay using the API Key.
- Preferred for production: centralised control, observability, and easier retries.
- Authorise is always backend-only with the API Key.
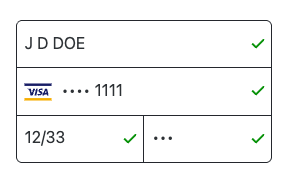
stack
Fields are stacked vertically, but related fields (e.g., Expiry + CSC) may appear inline within the stack. Best for narrow/mobile views.
row-minimal
All fields appear in a single horizontal row, with placeholders acting as labels. Very compact; ideal for inline flows where space is limited. Accessibility requires aria-labels or sr-only labels.

row-compact
Similar to row-minimal, but includes small visible labels above inputs while retaining the horizontal arrangement. Balances clarity with compactness.
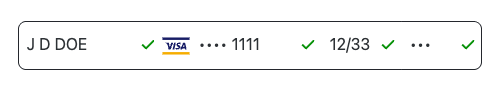
row
Default horizontal row layout. Fields are arranged side-by-side with full visible labels and consistent spacing. Best for wide containers where horizontal space is available.

column-compact
Fields are stacked vertically with reduced spacing, or small labels. A hybrid between full column and compact mobile layouts.

column
Full vertical layout, each field occupying the full width in its own row with visible labels. The most traditional and accessible form layout.
Elements API Reference
/api paths; your backend → CityPay with API Key) modes; only the network path differs.AttachOptions:{ intentId: string; token: string; idempotencyKey?: string }ConfirmOptions:{ intentId: string; autoHandle3DS?: boolean; idempotencyKey?: string; authorise?: { endpoint?: string; payload?: any } }ChallengePayload: 3DS challenge payload returned by your backend or CityPay.AttachResponse,ConfirmResponse,AuthoriseResponse: JSON responses reflecting intent state and challenge metadata.AuthOptions:{ intentId: string; endpoint: string; payload: any; idempotencyKey?: string }
Idempotency Always propagate the SDK’s idempotencyKey to backend → CityPay calls. It ensures safe retries and
consistent state transitions.
Minimal Example
import { CityPayElements } from '@citypay/elements'
const elements = new CityPayElements({
domainKey: DOMAIN_KEY,
})
const api = elements.cardForm('default', {
element: '#card-form',
language: 'en',
layout: 'stack',
theme: 'auto',
width: '100%',
height: 220,
})
await api.init()
await api.awaitReady()
elements.cardForm(id: string, options: CardFormOptions): ElementsApi
This creates and mounts the hosted Card Form (all fields inside CityPay-hosted iframes), returns an ElementsApi with lifecycle methods and events, and wires up transport (Direct vs Proxy) automatically.
Purpose
Mount a PCI-scoped, CityPay-hosted card UI on your page, ready to:
- Tokenise card data securely in-browser.
- Attach the token to a Payment Intent.
- Confirm the intent and handle 3-D Secure (3DS).
- Coordinate with your backend for authorisation and capture.
Signature
- id: A unique identifier for this form instance (e.g. "default"). You’ll use this to reference the instance in your code/tests.
- options: UI, mounting and behaviour settings (see below).
Throws a CityPayError if id or options are invalid.
Theme Tokens
You may override theme variables to match your design system:
Theme Tokens
type ThemeTokens = {
'--cpe-bg'?: string;
'--cpe-bg-alt'?: string;
'--cpe-fg'?: string;
'--cpe-fg-muted'?: string;
'--cpe-border'?: string;
'--cpe-border-subtle'?: string;
'--cpe-focus'?: string;
'--cpe-error'?: string;
'--cpe-success'?: string;
'--cpe-accent'?: string;
'--cpe-input-bg'?: string;
'--cpe-input-fg'?: string;
'--cpe-input-border'?: string;
'--cpe-input-placeholder'?: string;
'--cpe-radius'?: string | number;
'--cpe-gap'?: string | number;
'--cpe-padding'?: string | number;
'--cpe-control-height'?: string | number;
'--cpe-font'?: string;
}
Return: ElementsApi (for this form)
After cardForm(...), you’ll typically:
Initialisation
await api.init();
await api.awaitReady(); // handshake complete
const token = await api.tokenise();
Lifecycle & Events
When you call init() the component:
- Resolves and validates the mount container.
- Builds the iframe URL based on language and layout.
- Mounts the iframe with a fresh session uuid.
- Establishes a secure MessageChannel handshake.
Key events to wire up:
cpe:ready— fired once the handshake completes (pair with awaitReady()).cpe:change— field state updates.cpe:processing:start/cpe:processing:end— show/hide spinners.cpe:error— operation-scoped failure details.
Example
api
.onReady(() => setReady(true))
.onChange((s) => setPayEnabled(s.complete))
.onProcessingStart(() => showSpinner())
.onProcessingEnd(() => hideSpinner())
.onError((e) => notifyUser(e.detail?.message ?? 'Payment error'));
awaitReady(): Promise<void>
Waits for the iframe’s MessageChannel handshake before interaction.
Use Case 1: Late Payment Surcharge
const card = elements.cardForm('default', opts);
await card.init();
await card.awaitReady(); // safe to call tokenise()
Emits: cpe:ready.
Initialisation Requirements & Best Practice
- Mount container must exist and be visible. If using React/Next, create the form after the container is rendered (e.g. in useEffect with refs).
- CSP must allow CityPay origins for script, frame, and connect. Add frame-ancestors appropriately to prevent hostile embedding.
- Sizing: If you set width/height, allow enough space for validation messaging and accessibility focus rings. The component will enforce minimums.
- Language/layout: Choose a layout that avoids input crowding on smaller viewports. Consider 'row-compact' for tight spaces and 'stack' for clarity.
- Focus & a11y: Do not trap focus around the container; Elements manages field focus within the iframe. Provide clear error regions adjacent to the container for screen readers.
- SSR: Instantiate only client-side. Wrap in guards like if (typeof window !== 'undefined').
init(): Promise<void>
Initialises the form, event channels, and hosted fields.
Throws if the domain key or mount target is invalid.
tokenise(): Promise<string>
Tokenises card details inside the iframe. Returns a single-use token.
Emits:
cpe:processing:start/cpe:processing:endcpe:erroron failure
Usage
const token = await card.tokenise();
// send token + checkout data to backend
attach(options: AttachOptions): Promise<AttachResponse>
Associates a token with an existing Payment Intent.
- Direct: SDK → CityPay (Domain Key).
- Proxy: SDK → Merchant backend
/attach, then backend → CityPay.
Emits: cpe:attach:start / cpe:attach:end, cpe:error.
confirm(options: ConfirmOptions): Promise<ConfirmResponse>
Confirms the intent and handles 3DS if required.
autoHandle3DS: true→ SDK renders challenge automatically.- Optionally
authorise: { endpoint, payload }triggers backend authorisation after confirm.
Emits:
cpe:confirm:start/cpe:confirm:endcpe:challenge:start/cpe:challenge:end(if 3DS)cpe:erroron failure
confirmAfterChallenge(options: Omit<ConfirmOptions, 'autoHandle3DS'>): Promise<ConfirmResponse>
Used for manual 3DS flows. Call after presenting the challenge yourself.
handle3DSAuthentication(challenge: ChallengePayload): Promise<string>
Starts a 3DS challenge from a payload provided by your backend (Proxy mode).
Emits: cpe:challenge:start / cpe:challenge:end, cpe:error.
authoriseViaBackend(options: AuthOptions): Promise<AuthoriseResponse>
Helper to call your backend to perform authorise.
- Always server → CityPay with API Key.
- Emphasise idempotency for retries.
Emits: cpe:authorise:start / cpe:authorise:end, cpe:error.
reset(): Promise<void>
Clears field state and validation, e.g., after a decline.
Event API
on(type, listener): this– chainable listener registration.onChange,onReady,onProcessingStart,onProcessingEnd– convenience hooks.addEventListener/removeEventListener– DOM-style APIs.
destroy(): void (optional)
Tears down the iframe and listeners. Use in SPA route changes to prevent leaks.
Direct Mode
const elements = new Elements(DOMAIN_KEY, {mode: 'direct'});
const card = elements.cardForm('default', options);
await card.init();
await card.awaitReady();
const token = await card.tokenise();
const {intentId} = await api.createIntent({amount, currency, orderRef});
await card.attach({intentId, token});
await card.confirm({intentId, autoHandle3DS: true});
const auth = await card.authoriseViaBackend({
intentId,
endpoint: '/api/payments/authorise',
payload: {amount, currency, orderRef}
});
Proxy Mode
const elements = new Elements(undefined, {
mode: 'proxy',
proxy: {basePath: '/api/payments'}
});
const card = elements.cardForm('default', options);
await card.init();
await card.awaitReady();
const token = await card.tokenise();
const {intentId} = await api.intent(); // your backend
await card.attach({intentId, token}); // hits /api/payments/attach
await card.confirm({intentId}); // hits /api/payments/confirm (backend returns 3DS payload if needed)
const auth = await card.authoriseViaBackend({
intentId,
endpoint: '/api/payments/authorise',
payload: {amount, currency, orderRef}
});